In the realm of computer storage, choosing between a Solid State Drive (SSD) and a Hard Disk Drive (HDD) can significantly impact your device’s performance, reliability, and user experience. Both SSDs and HDDs serve the same fundamental purpose—storing your data—but they do so in vastly different ways. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding their differences and making an informed decision:
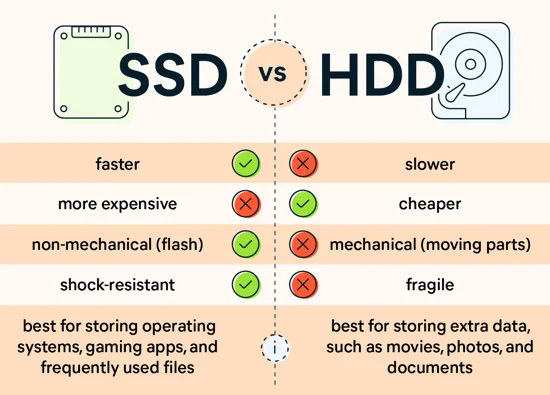
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Technology and Construction:
- HDD: Hard Disk Drives are mechanical devices that use spinning disks (platters) coated with a magnetic material. Data is written and read using a mechanical arm with a read/write head. The speed is determined by the rotational speed of the disks (typically 5400 RPM or 7200 RPM).
- SSD: Solid State Drives, on the other hand, have no moving parts. They store data on interconnected flash memory chips, similar to the ones used in USB drives. This design allows for much faster data access and transfer speeds compared to HDDs.
2. Performance:
- HDD: Traditional HDDs are slower than SSDs in terms of both data access speed and boot-up time. This is because they rely on the mechanical movement of the disk and the read/write head.
- SSD: SSDs excel in performance due to their non-mechanical nature. They offer significantly faster data transfer rates, quicker boot times, and faster file access speeds. This makes SSDs ideal for applications where speed is crucial, such as gaming or video editing.
3. Durability and Reliability:
- HDD: Because HDDs have moving parts, they are more prone to mechanical failure over time. The spinning disks and moving read/write head can wear out or become damaged, leading to data loss.
- SSD: SSDs are generally more durable and reliable than HDDs. They are resistant to physical shock, operate silently, and have lower access times. However, like all electronic devices, they can fail due to factors such as electrical issues or firmware corruption.
4. Capacity and Cost:
- HDD: HDDs offer larger storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte compared to SSDs. If you need terabytes of storage without breaking the bank, HDDs are still a viable option.
- SSD: SSDs are more expensive per gigabyte of storage compared to HDDs. However, the price gap has been narrowing, and SSD prices have become more competitive over the years. They are available in a range of capacities suitable for various needs.
5. Choosing the Right Drive:
- Considerations: When choosing between an SSD and an HDD, consider your specific needs:
- Performance: If speed is crucial for your tasks, such as gaming or professional video editing, opt for an SSD.
- Storage Capacity: If you need large storage capacities at an affordable price, HDDs are still a good choice.
- Budget: SSDs are more expensive but offer better performance. Evaluate your budget and storage requirements to find the right balance.
- Usage: Consider how you use your computer. For everyday tasks like web browsing and document editing, an SSD can offer a noticeable improvement in responsiveness.
Conclusion:
The choice between SSD and HDD ultimately depends on your priorities—whether it’s speed, storage capacity, or budget. SSDs provide superior performance and durability but at a higher cost per gigabyte. HDDs offer larger capacities at a lower price but with slower performance. Assess your needs and budget carefully to make the best decision for your computing experience.